memory#
Description#
This behavior is a ZebFront implementation of a strain range memory
isotropic hardening model described by Lemaitre and Chaboche
[M8]. The model has 2 non-linear kinematic
hardening components (coefficients C1, D1, C2, and
D2), and a Norton type flow law (coefficients K and
n).
The yield criterion is given by
where \(J(\diamond) = \sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}\diamond^{dev}:\diamond^{dev}}\), and \(\diamond^{dev}\) is the deviatoric part.
The viscoplastic flow rule is
The constitutive equations are:
where \(\tenf{\mathbb{C}}\) is the elasticity fourth-rank tensor. The evolution equations for kinematic hardening internal variables are
where \(\ten n=\dfrac{3}{2}\dfrac{\ten \sigma^{dev}-\ten X_1-\ten X_2}{J(\ten \sigma-\ten X_1-\ten X_2)}\) is the normal to the loading surface \(f=0\).
As observed for 316L stainless steel [M8], the asymptotic value of the cyclic hardening (\(Q\)) may depend on the strain amplitude. Two additional variables are added to keep track of the plastic strain range: the center \(\ten{\xi}\) and the radius \(q\) of the plastic strain enveloping surface \(F\),
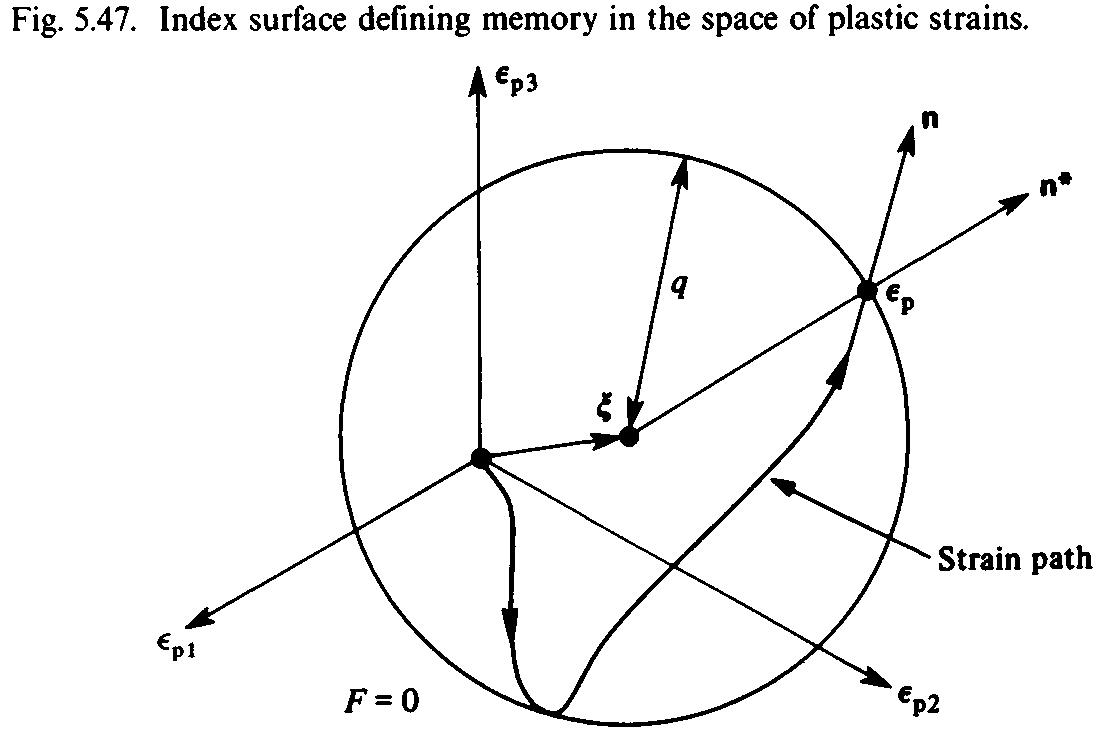
The enveloping surface of previous strains will move only when the current strain state is on the surface \(F=0\), and that the flow occurs in the direction external to the surface. The evolution equations are given by:
where \(H(x)=1\) if \(x\geq 0\), \(H(x)=0\) if \(x<0\). The variable \(\eta\) is determined by the consistency condition \(dF=0\):
where \(\ten n^*\) is the normal to the index surface \(F = 0\):
The asymptotic value \(Q_{sat}\) of isotropic hardening depends on the variable \(q\) as:
Syntax#
***behavior memory
\(~\,\) **elasticity <ELASTICITY>
\(~\,\) **model_coef
\(~\,~\,~\,\) coefs
Example#
***behavior memory
**elasticity isotropic
young 200000.
poisson 0.3
**model_coef
n 5.
K 50.
C1 1000.0
D1 20.
C2 12000.
D2 120.
R0 50.
b 25.
Q0 25.
Qsat 400.
mu 50.
***return
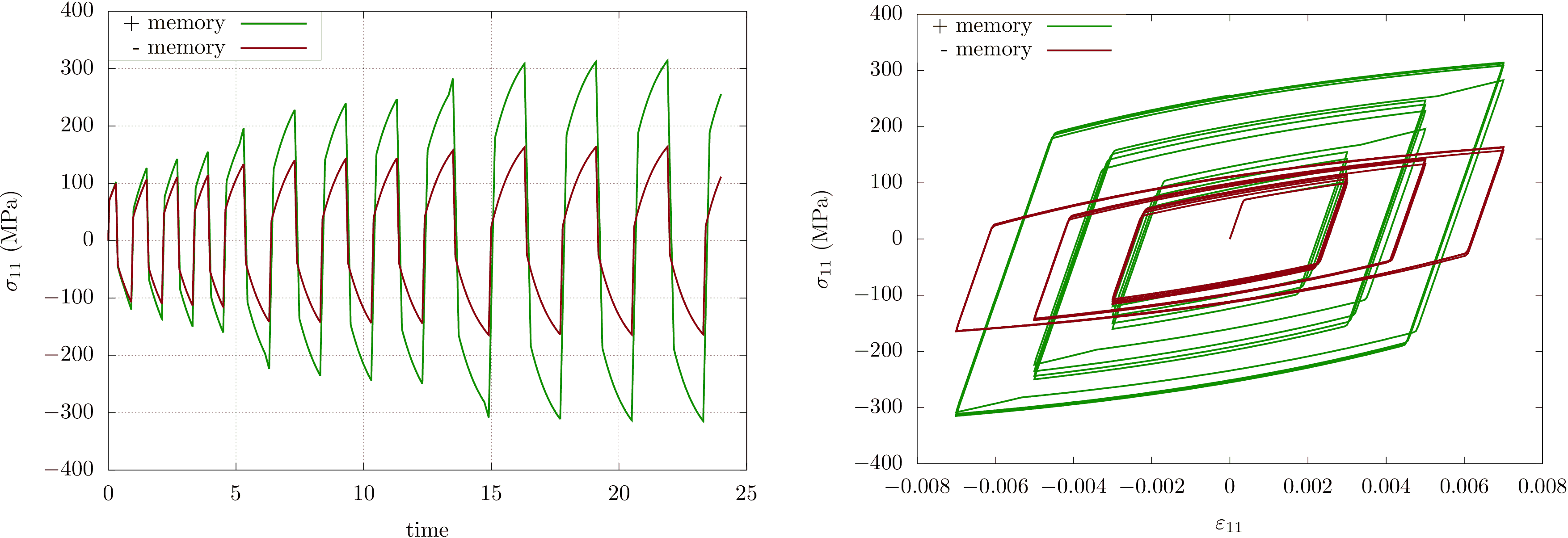
Fig. 12 A cyclic tension/compression loading with different strain amplitudes (4 cycles fo each amplitude) for models with and without memory.#
Note
To describe strain range memory effect, one can also use
nonlinear_with_memory isotropic hardening with gen_evp behavior as:
***behavior gen_evp
**elasticity isotropic
young 200000.
poisson 0.3
**potential gen_evp ev
*flow norton
n 5.
K 50.
*isotropic nonlinear_with_memory
R0 50.0000
b 25.0000
Q0 25.0000
Qsat 400.000
mu 50.0000
*kinematic nonlinear
C 1000.00
D 20.0000
*kinematic nonlinear
C 12000.00
D 120.0000
***return